Rappi Payless Integration Guide
What is Rappi Payless?
Rappi Payless is a card-free payment method exclusive for our pickers (personal shoppers and couriers).
It enables point of sales systems (POSs) to process Rappi orders using payment codes generated from our pickers' mobile apps. Those payment codes are presented in the form of barcodes or QR codes.
Rappi Payless eliminates card transaction fees. It also simplifies conciliation and reporting, reduces checkout time, and eliminates operational issues related to releasing funds to debit cards.
Payless Flow
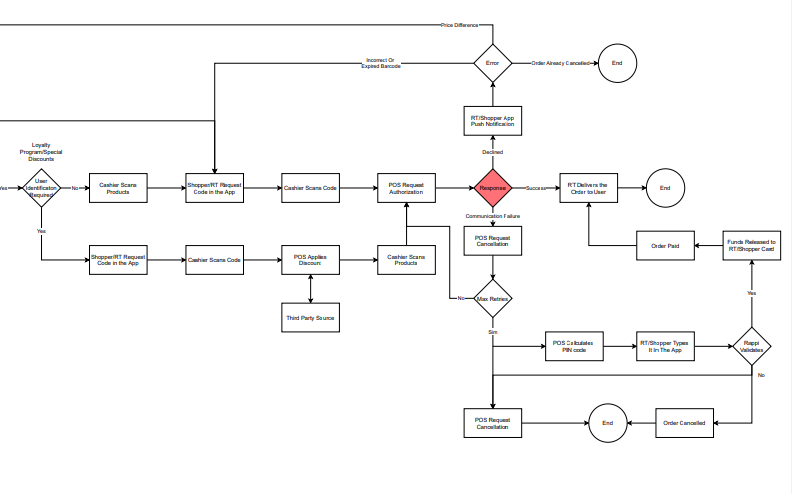
Click here do download Payless Flow document.
Take some time to analyze and understand all the possible scenarios the POS system will have to implement for a succesfull integration.
Integration Checklist
Upon successfully implementing Rappi Payless, your solution is expected to achieve the following:
Ingest and process Rappi Payless payment codes either in the form of barcodes, QR-codes, or manually keyed-in.
Send payment authorization requests to Rappi including all required details.
Properly handle successful and declined transactions.
Handle request timeouts with automatic retries.
Switch to the fallback flow when communication with Rappi is unavailable.
Daily conciliation of your transactions authorized by Rappi.
Introduction
This article provides an overview of Rappi Payless. Expect to learn more about:
- our picker's experience with Rappi Payless,
- the regular and fallback payment flows,
- how to retrieve information to feed your conciliation process,
- how to consume our sandbox methods to setup your test environment and run manual and automated tests on your integration.
Customer Places a New Order
| 1. Customer places a new order Depending on the store configuration, an algorithm decides whether the order will be fulfilled by a personal shopper or a courier. | |
| 2. Picker goes through the shopping list From the product list, the picker must mark each product as "found", "not found", or "replaced". Pickers can't advance to payment with pending products on the shopping list. | |
| 3. Picker arrives at the checkout At this point, the picker app is in payment mode, generating new codes every 30 seconds. |
Shopper Pays with Payless
| 4. (Optional) POS retrieve customer's identification Useful when POS need user identification to apply loyalty markdown and promotions. Payment code is scanned from the picker's device to retrieve order details.. | |
| 5. Cashier scans all products The POS applies markdowns and promotions, and calculates the bill. | |
| 6. Payment code is scanned from the picker's device The cashier has the option to scan a QR code, a barcode, or manually key-in a six-digit code. Learn more about the Rappi Payless payment code here. If the POS already has the barcode gathered before the scan of products when retrieving customer's identification, there's is no need to scan the barcode again. | |
| 7. POS sends the purchase details to Rappi This is an HTTP request to our Payment Authorization endpoint. If successful, the POS will receive a transaction authorization token in response. | |
| 8. Picker takes a snapshot of the receipt The order is ready for delivery. |
The Rappi Payless Barcode
The Rappi Payless barcode (also referred to as payment code) is a random number associated with a unique order identifier in our database.
Barcodes are refreshed every 30 seconds on our pickers' apps payment views. They remain active for another 30 seconds when Rappi's backend finally expires them. Therefore, a barcode total time live (TTL) is one minute (60 seconds).
AUTO RETRIES ON TIMEOUTS
The barcode's TTL is 60 seconds. It's important to consider this information when implementing automatic retries in response to communication failures or timeouts between your POS and Rappi's backend.
Automatically Detect the Payment Method
We have created an optional configuration that allows retailers to specify a 2-letter prefix that will be prepended to each barcode we generate.
The common use for this configuration is having the POS automatically identify the payment method as Rappi Payless, without requiring the cashier to enter any commands from the keyboard.
Rappi Payless Fallback
Besides being used in the payment authorization request, the barcode's sequence of digits is also an input variable for the verification algorithm on the fallback flow. This is detailed in the section about communication failures.
Payment Authorization Requests
A successful transaction will always return an HTTP status code 200 and includes an authorization token in the response body. Both the barcode and the authorization token (or authorization code) for each successful transaction MUST be stored on the retailer's side for conciliation purposes.
Declined Authorizations
Although there are few reasons that lead a transaction to be declined by Rappi, those aren't yet defined by reason codes, and we don't expect the POS to expose this information. On each declined transaction, the picker receives a push notification with instructions to adjust the order before retrying the payment.
Malformed payment authorization request
There might be missing required properties or inconsistent property types in your payment authorization.
The requested amount for the payment exceeds the authorized threshold for an order
This scenario may be caused by unreported price differences pushing the requested amount past the order authorization threshold or products requested by the customer via chat were not properly included in the order by the picker.
With each declined transaction, the pickers receive push notifications on their apps, advising them about inconsistencies in the order and asking them to make the necessary adjustments before retrying. Once adjusted, the order shouldn't be rejected a second time.
Unacceptable orders
Orders that receive the error message
unacceptable_ordermay have been canceled by the customer (and due to a momentary connectivity issue, the picker app wasn't synced), they may have already been paid for, or the courier is trying to purchase the products at a different retail partner.Invalid barcodes
Most of the time, invalid barcode scenarios are associated with fraud attempts. A screenshot of the barcode screen is taken and the payment is declined; either because that barcode is expired or it has already been applied to another payment.
Handling Communication Failures
Best practice on Rappi Payless implementations mandates having an automatic retry at the POS whenever a communication failure occurs i.e., when the POS doesn't receive a response to its payment authorization request.
Example: The cashier enters a command on the POS to send out a payment authorization request to Rappi. If your requests are configured to timeout after 5 seconds, you may safely have up to 6 automatic authorization attempts within the barcode TTL.
The timeout setting is configurable at the discretion of each retailer, taking into account the latency of their private networks.
Falling Back to Debit Cards
If, even after exhausting retries, the POS is still unable to receive a response for a payment authorization request, the fallback flow MUST kick-in. This is required of ANY Rappi Payless implementation before being released to production.
In this scenario, pickers need to notify Rappi that they need funds released to their debit cards to pay for an order. Since their app is unaware of what's going on between the POS and our backend, the following process validates Rappi can safely release funds to a picker.
| 1. POS tells the cashier something isn't right When the POS confirms a communication failure, it will calculate a random pin code and display on its screen with the message "Communication with Rappi is unavailable. The Rappi staff needs this code to pay with debit card". No connectivity is required to calculate the pin code. | |
| 2. Picker enters the pin code on the app From the payment view on the app, our pickers have an option labeled "The Code Doesn't Work". Pressing this button, they're instructed to insert the pin code given by the cashier/POS to have funds released to their debit cards. | |
| 3. Rappi checks it's a valid pin code Since both Rappi and the POS are using a common algorithm to calculate the pin code, this validation can happen even when there's no connectivity between the parts. | |
| 4. Picker pays for the purchase with a debit card The pin code validation triggers the regular flow that releases funds to pickers debit cards |
IT SHOULD BE A RARE EXCEPTION
The alternative flow allowing card payments is a must have, but should be a rare exception. Our main KPI in Rappi Payless is having 99.9% of transactions processed by our authorization engine. It means the fallback flow should only kick-in once in every 1000 orders processed.
Calculating the Pin Code
Allowing pickers to switch the payment method to debit card without a proper validation would play against the purpose of implementing Rappi Payless; and prevent both Rappi and its partner retailers from extract the most benefits out of this technology.
Therefore, calculating and validating the pin code when there's no connectivity between client and server requires both parties to use a common algorithm and input variables that are available to both.
The algorithm takes two input variables: the current_date formatted as YYMMDD and the barcode. The pin code is resolved by multiplying the current date by the barcode and extracting the last 6 digits of the result. The pin code is a string and not an integer since its leading digit(s) might be zeros.
IN CASE THE PIN CODE FAILS
If the pin code is not validated by the app, the shopper has 5 retries to enter the code correctly. If even the retries fail, the order is cancelled.
Sandbox Setup and Usage
Our sandbox operations were created to accelerate our partners' development and testing, and it's proven to drastically reduce the integration lead time. This is a six-step process. Any store_id can be used on the methods listed in our sandbox documentation.
REMEMBER TO USER THE PROPER URL FOR SANDBOX/PRODUCTION
Please check proper URLs in Servers and Authentication.
Upload Product Catalog
PUT /testing/products
Sandbox This endpoint uploads a catalog of products to your Sandbox environment. It's required to allow the creation of orders for development, testing automation, and quality assurance purposes.
The upload operation performs an upsert, meaning any uploaded products matching an SKU identifier (retail_id) in Rappi's database will be updated with fresh information received in the file, otherwise the new product will be created.
PRODUCT CATALOG IN EXCEL FORMAT
Please use this schema
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
body required | object | body | Your sandbox product catalog must be provided in an Excel (.xlsx) file. It must be smaller than 2 MB and adhere to the following schema. |
» file required | string(binary) | body |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–file uploaded |
400 Bad Request | There was a problem with the file you uploaded, e.g., "The max file size is 2MB". |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |
Status Code 200
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» message string | The success message will include a file processing id (int) you can use to verify the status of your catalog creation or update, e.g., "The file is being processed. Please check the results using the id 32". |
Status Code 400
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 400, |
» message string | Free text describing the error enums: |
Verify Product Catalog Upload
GET /testing/products/upload-results/{resultId}
Sandbox This endpoint verifies the status of a product catalog creation or update in your sandbox.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resultId required | integer | path | The operation identifier returned from a catalog upload. |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success response |
400 Bad Request | Catalog processing is still running. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |
Status Code 400
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 400, |
» message string | Free text describing the error enums: |
IMPORTANT!
Subsequent uploads overwrite existing products.
At this point, you're ready to start running test cycles. Each test cycle is made up of multiple orders and four steps. Each order in the test cycle simulates a different scenario. You're not required to consume every single order from each set you generate, but it's important to validate that all scenarios are properly handled.
Generate Dummy Orders
POST /testing/orders
Sandbox This endpoint generates a set of dummy orders with multiple scenarios for your testing and QA routines.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
body required | object | body | |
» store_id required | integer | body | Unique store identifier in your systems; usually the store identifier from your ERP. |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–set of dummy orders returned; each scenario in the response body will adhere to the schema{ "order_id": "string", "shopper": "string" }. |
400 Bad Request | The request failed; more details in the response body. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |
Status Code 200
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» valid object | |
» invalid_state object | |
» invalid_storekeeper object | |
» different_retailer object | |
» invalid_high_price object | |
» invalid_low_price object |
Status Code 400
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 400, |
» message string | Free text describing the error enums: |
This operation generates a set of dummy orders for different scenarios:
valid | The transaction will be authorized if the correct products are scanned. |
invalid_state | The transaction will be declined. The order state in our database isn't in_payment. This simulates when a picker tries to pay for an order... before the shopping list is resolved (which shouldn't be possible); ... that has already been paid for (at another store or POS); ... that has already been canceled (but syncing with the picker app might have failed). |
different_retailer | The transaction will be declined. It simulates a picker trying to pay with a barcode generated for a different retailer. |
invalid_high_price | The transaction will be declined. It simulates price differences that were not adjusted by the picker before arriving at the cashier. |
invalid_storekeeper | This case is marked for deprecation. |
invalid_low_price | This case is marked for deprecation. |
Generate Payment Code
This is the same operation used by our picker apps to render the barcodes on the payment view. The payment code path parameter isn't only part of the payment authorization request, but is also used when you need to retrieve the details of an order.
POST /pos/orders/{order_id}/barcode
Sandbox This endpoint generates a payment code (barcode) associated with an order in our database.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
order_id required | integer | path | Unique identifier of an order created by a customer in the sandbox environment, the id of your dummy orders. |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–barcode object returned. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token |
404 Not Found | The resource or record you're requesting doesn't exist. |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |
Status Code 200
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» order_id string | |
» barcode string | |
» status string | |
» created_at string(date-time) | |
» sent_at string(date-time) | |
» expires_at string(date-time) | |
» show_until string(date-time) | |
» prefix string | |
» refreshed boolean | |
» owner_id integer | |
» qr object | |
»» id string | |
»» order_id string | |
»» barcode string | |
»» status string | |
»» created_at string(date-time) | |
»» sent_at string(date-time) | |
»» expires_at string(date-time) | |
»» show_until string(date-time) | |
»» prefix string | |
»» owner_id integer | |
»» refreshed boolean |
Retrieve Order Details
GET /pos/v3/payments/{barcode}/order
This endpoint is invoked when the POS needs to retrieve the order details from Rappi before check-out starts. It SHOULD be used in scenarios where the POS needs the customer's identification or loyalty program number to apply exclusive discounts.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
x-rappi-country required | string | header | The country of operation for a partner retailer. It accepts two-letter country codes in the ISO 3166 alpha-2 format. Accepts: AR, BR, CL, CO, CR, EC, MX, PA, PE, UY |
x-rappi-channel required | string | header | This identifies the type of client interacting with the cashier in store. Accepts: B2B |
barcode required | string | path | The payment code scanned from a picker's mobile (or manually keyed-in). This code will always be a random number associated with an order. |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–details of an order associated with the scanned barcode returned. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token |
404 Not Found | The resource or record you're requesting doesn't exist. |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |
Status Code 200
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» orderId string | Unique identifier of an order in Rappi. |
» paymentMethod string | Payment method. |
» created_at string(date-time) | UTC timestamp when the customer placed the order. |
» updated_at string(date-time) | UTC timestamp when the order was updated. |
» ready_at string(date-time) | UTC timestamp when the order was ready. |
» delivery_schedule string(date-time) | UTC timestamp for the delivery schedule. |
» currency string | Currency. |
» amount double | Amount. |
» store_id string | Store ID. |
» customer_preference string | Customer Preference. |
» customer object | |
» delivery_address object | |
» basket array |
Payment Authorization
POST /pos/v3/payments/{barcode}/authorize
This endpoint is invoked when the point of sale (POS) must provide a payment authorization request. The transaction may be declined if Rappi finds inconsistencies against the order details in its database.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
x-rappi-country required | string | header | The country of operation for a partner retailer. It accepts two-letter country codes in the ISO 3166 alpha-2 format. Accepts: AR, BR, CL, CO, CR, EC, MX, PA, PE, UY |
x-rappi-channel required | string | header | This identifies the type of client interacting with the cashier in store. Accepts: B2B |
barcode required | string | path | The code scanned from a picker's mobile (or manually typed-in). This code will always be a random number associated with an order (see fall back option for further information. |
body required | object | body | |
» currency | string | body | Currency. |
» amount required | number | body | Amount to be collected by this payment. |
» store_id | string | body | store_id. |
» terminal_id | string | body | Unique store identifier in your systems; usually the store identifier from your ERP. |
» terminal_transaction_id | string | body | Unique transaction identifier in your systems; usually the store identifier from your terminal. |
» total_taxes | number | body | Total amount of taxes collected on this purchase. |
» total_discount required | number | body | Total discount SHOULD be the sum of simple product markdowns, single or multi SKUs bundle discounts, and any discounts associated with the form of payment. |
» basket | [object] | body | |
» metadata object |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–transaction authorization approved by Rappi. |
400 Bad Request | Transaction authorization declined. A dispersion fallback must be performed using the pincode. The POS must review the payless development to adjust the request before accepting more orders. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token. A dispersion fallback must be performed using the pincode. The POS must review the payless development to adjust the request before accepting more orders. |
403 Forbidden | Transaction authorization forbidden. This error occurs when the barcode and the order to authorize belong to another retailer; it can happen as the result of a badly typed barcode. A dispersion fallback must be performed using the pincode |
404 Not Found | Invalid barcode error. This error occurs when the barcode used to authorize the order does not exist or has expired. POS must validate that the payment code is correct. RT must generate a new QR code |
406 Not Acceptable | Transaction authorization declined. Ask the RT for the Shopper to adjust the order. This error occurs due to the difference between prices and products in the cart. |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. A dispersion fallback must be performed using the pincode. |
Status Code 200
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» message string | The transaction authorization returned on this property is represented by a JWT token. |
Status Code 400
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 400, |
» message string | Human readable description of the error enums: |
Status Code 403
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 403, |
» message string | Human readable description of the error enums: |
Status Code 404
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 404, |
» message string | Human readable description of the error enums: |
Status Code 406
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
» code integer | The HTTP error code enums: 406, |
» message string | Human readable description of the error enums: Unacceptable order, |
Payment Cancellation
POST /pos/v3/payments/{barcode}/cancel
This endpoint is invoked when the point of sale (POS) needs to cancel a payment authorization request.
Cancellation limit
Be aware that it's only possible to cancel orders in the same day they were authorized.
Request Example
Request Parameters
| Parameter | Type | In | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
x-rappi-country required | string | header | The country of operation for a partner retailer. It accepts two-letter country codes in the ISO 3166 alpha-2 format. Accepts: AR, BR, CL, CO, CR, EC, MX, PA, PE, UY |
x-rappi-channel required | string | header | This identifies the type of client interacting with the cashier in store. Accepts: B2B |
barcode required | string | path | The code scanned from a picker's mobile (or manually typed-in). This code will always be a random number associated with an order (see fall back option for further information. |
body required | object | body | |
» currency | string | body | Currency. |
» amount required | number | body | Amount to be collected by this payment. |
» store_id | string | body | store_id. |
» terminal_id | string | body | Unique store identifier in your systems; usually the store identifier from your ERP. |
» terminal_transaction_id | string | body | Unique transaction identifier in your systems; usually the store identifier from your terminal. |
» total_taxes | number | body | Total amount of taxes collected on this purchase. |
» total_discount required | number | body | Total discount SHOULD be the sum of simple product markdowns, single or multi SKUs bundle discounts, and any discounts associated with the form of payment. |
» basket | [object] | body | |
» metadata object |
Responses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
200 OK | Success–transaction authorization approved by Rappi. |
400 Bad Request | Transaction authorization declined. |
401 Unauthorized | The request was signed with an invalid or expired authorization token. |
403 Forbidden | Transaction authorization forbidden. |
404 Not Found | Invalid barcode error. |
500 Internal Server Error | This is an issue with the server, not the request. |